
Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Checklist 'taxonomie van Bloom' Toelichting Een van de meest gebruikte manier om verschillende kennisniveaus in te delen, is op basis van de taxonomie van Bloom. Deze is tussen 1948 en 1956 ontwikkeld door de onderwijspsycholoog Benjamin Bloom, als algemeen model voor de doelstellingen van het leerproces. De taxonomie onderscheidt verschillende.

Taxonomie van bloom uitleg denkvaardigheden
In Bloom's revised taxonomy, the level of synthesis has been added. This refers to students' ability to combine information from different sources. The video below outlines Bloom's taxonomy and explains ho wit may be used in the development of assignments. UvA TLC good practices 004 taxonomie van Bloom. Back to Assessment.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Bloom's taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used for classification of educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning.

Taxonomie van Bloom Schoolupdate academie
Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchical model of learning objectives. The base layers focus on basic understanding, while the upper levels pivot towards analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These "higher order" stages beckon students to engage actively with material, connecting dots and drawing insightful conclusions.

Blooms Taxonomy Display, Blooms Taxonomy Poster, Blooms Taxonomy Verbs, Blooms Taxonomy
Familiarly known as Bloom's Taxonomy, this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching. The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Familiarly known as Bloom's Taxonomy , this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers, college and university instructors and professors in their teaching. The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
De uitleg. De taxonomie van Bloom, ontwikkeld door Benjamin Bloom, een psycholoog aan de universiteit van Chicago, is een classificatie van de verschillende doelstellingen die onderwijzers of trainers kunnen gebruiken bij het formuleren van leerdoelen voor hun studenten of cliënten. De taxonomie van Bloom drukt het cognitieve leerproces uit in.
voorbeeldvragen Bloom leeractief
Benjamin Bloom ontwierp een taxonomie voor doelen in het onderwijs, en eerlijk gezegd: het staat op het lijstje van meest gevraagde factchecks. Dit zou de taxonomie samengevat zijn: Maar, je merkte het wellicht al, ik gebruikte bewust voorwaardelijke wijze. De voorbije weken is er behoorlijk wat deining ontstaan in de Angelsaksische wereld rond deze taxonomie.

digitale taxonomie van Bloom 21st century skills, Brain learning, 21st century classroom
Taxonomie van Bloom (bron: SLO, 2015) De taxonomie van Bloom kan onder andere gebruikt worden als hulpmiddel bij het formuleren van leerdoelen en hieraan gerelateerde acties en producten, waarmee deze doelen gerealiseerd kunnen worden. Als leerkracht wil je een rijke leeractiviteit creëren voor leerlingen.

Taxonomie van bloom voor een rijke leeromgeving Artofit
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with collaborators Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals: Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Familiarly known as . Bloom's Taxonomy, this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Bloom's Revised Taxonomy for Learning Objectives. This work is adapted from David R. Krathwohl (2002) A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy: An Overview, Theory Into Practice, 41:4, 212-218, DOI: 10.1207/s15430421tip4104_2, and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
/5857112597_eae735e2af_o-58ac97533df78c345b72a141.jpg)
How to Construct a Bloom's Taxonomy Assessment
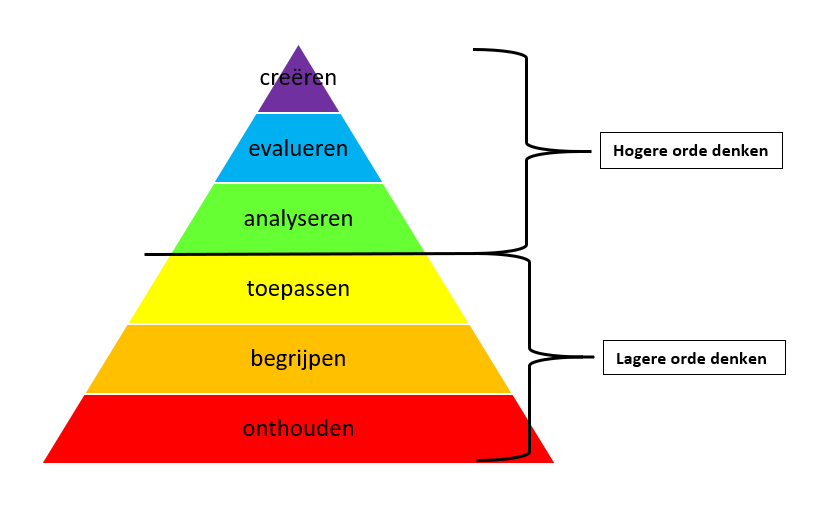
De taxonomie van Bloom is een handig overzicht waarin volgens enkele auteurs het verschil wordt gemaakt tussen 'hogere orde denken' en 'lagere orde denken'. Simpel gezegd: reproduceren en toepassen is makkelijk, pas vanaf analyse en synthese wordt het interessant. Het hoogste niveau is 'creëren'. Lagere orde vragen zijn vragen die.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
Formuleren van Leerdoelen- Hilde ter Horst en Riet Martens (aan te raden, bevat ook voorbeelden van leerdoelen) Werkwoorden bij beheersingsniveau van Bloom; Herziene Taxonomie van de leerdoelen van Bloom- van de Kamp, Universiteit van Amsterdam; References. Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of Bloom's taxonomy: An overview.

Taxonomie van Bloom Kosmisch concreet Nederland
In 2001 Bloom's taxonomy was revised by a group of cognitive psychologists, led by Lorin Anderson (a former student of Bloom). To update the taxonomy to reflect 21st century work the authors used verbs to re-label the six categories and included "action words" to describe the cognitive processes by which learners encounter and work with.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
In APA format, in-text uses author-date format. When referencing the entire work or an idea from Bloom's Taxonomy, your citation does not need a specific page number. If you're quoting directly or paraphrasing you must include page numbers. In-text citations for Bloom's Taxonomy look like (Bloom, 1956) or (Bloom, 1956, p. 200).

De Taxonomie van Bloom l Blog l September Onderwijs
One of the most powerful aspects of Bloom's Taxonomy is that it quote you, as an educator, who ability to construct a curriculum to valuate objective learning outcomes, contains advanced didactic targets liked critical thinkers. Pre-created Bloom's User questions can also make planning discussions, learning activities, and formative assessments much easier.